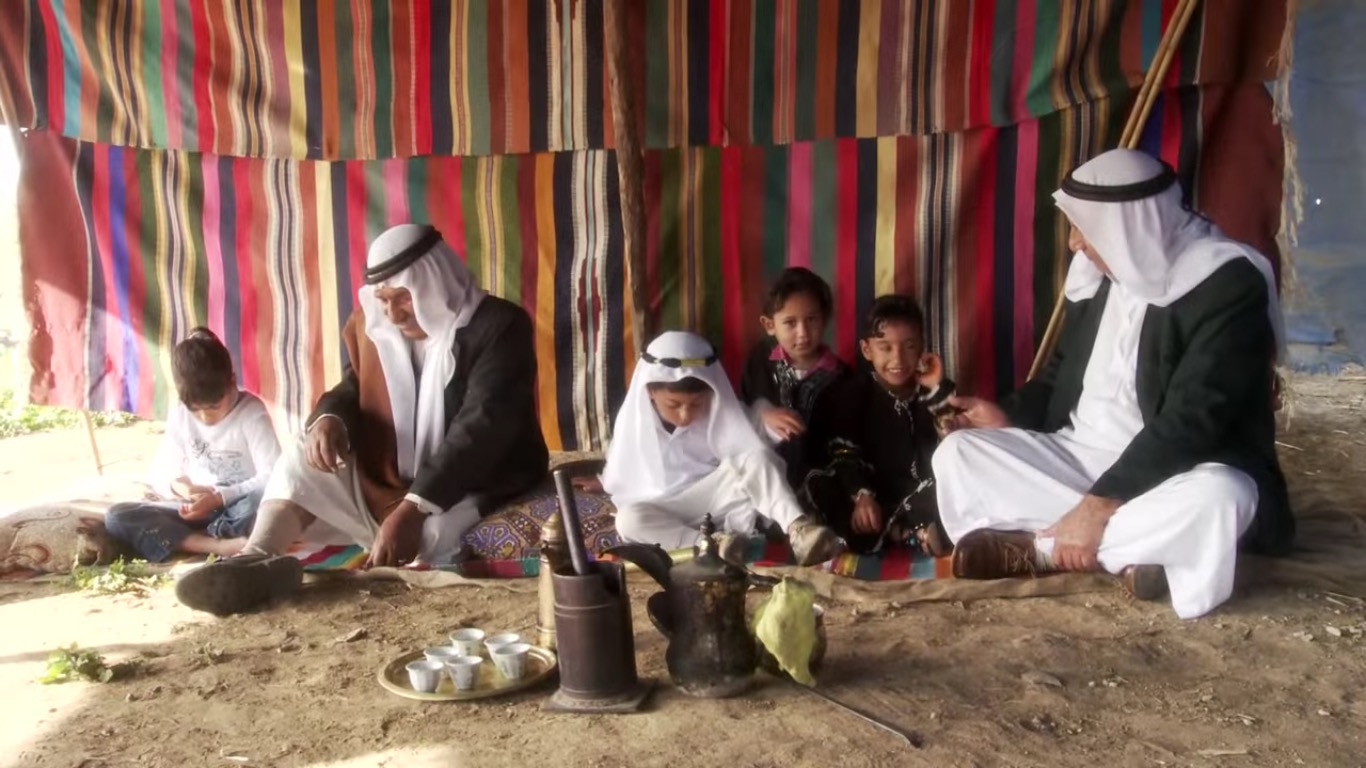
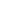
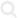A Bedouin family in a still from the Sustainability Laboratory's short film Project Wadi Attir. Photo courtesy Project Wadi Attir
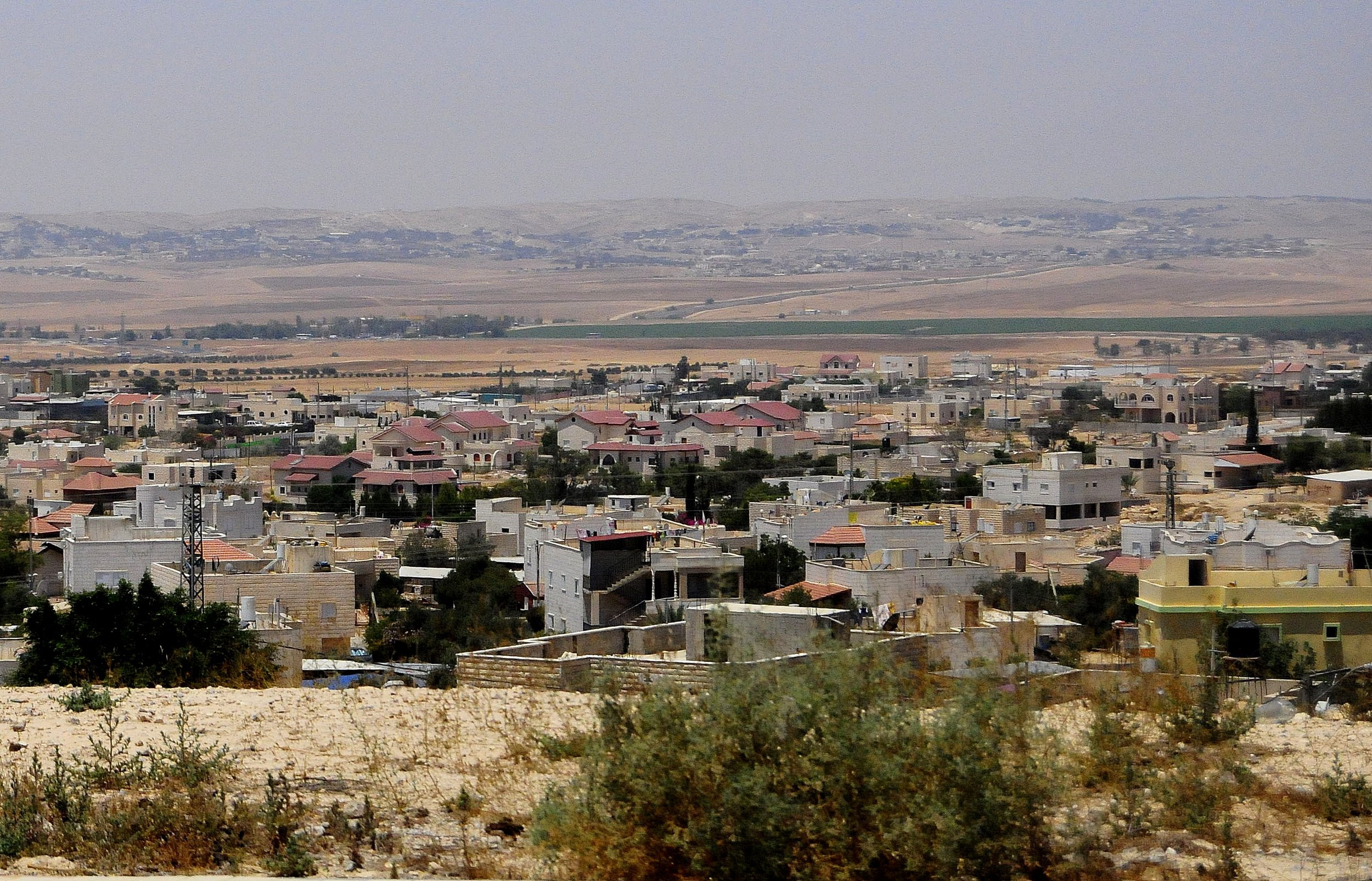
Project Wadi Attir is located in the northern Negev near the Bedouin town of Hura. It was founded by Michael Ben-Eli, who heads a global initiative called the Sustainability Laboratory. The project’s aim is to find a way to combine Bedouin culture and experience with progressive notions of sustainability and “green” technologies—looking at renewable-energy production, recycling, land stewardship, and much more.
“Project Wadi Attir serves as a model for Jewish-Bedouin collaboration. “It is good for the people. It makes them feel good as citizens. It makes them proud to be part of Israel.
”
The concept for the project was born in 2007 when Ben-Eli and his colleague Josh Arnow paid a visit to Ben-Gurion University and the Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research—centers outfitted with astonishing technologies and facilities, where much of Israel’s world-class research into desert living is being conducted. But during that visit, Ben-Eli and Arnow also saw the harsh living conditions of the growing Bedouin community, trying to make its way in a land of increasing Westernization and urban sprawl. “It did not seem right,” Ben-Eli has observed, “that full citizens in a country like Israel would live in desperate circumstances, when there were such incredible technologies being developed nearby.”
Ben-Eli met with Muhammad al-Nabari, the forward-thinking mayor of Hura, and they teamed up to bring Project Wadi Attir to light. A joint effort between Ben-Eli’s Sustainability Laboratory and the Hura Municipal Council, the project is decidedly holistic in its approach: dealing with social, economic, environmental, as well as tech considerations. Collaborators include Bedouin community members, university scientists and researchers, local nonprofit organizations, a nearby kibbutz, government agencies, and private-sector companies. The hope is that this new vision of environmentally sound development—beneficial to all parties—may impact the entire Middle East region as well as other parts of the world.
At the Project Wadi Attir farm, Bedouins tend goats and sheep organically for the production of dairy products. They grow medicinal plants and herbs (based on traditional Bedouin healing methods), and have developed a line of health products for sale on the mainstream market. Indigenous vegetables were once an important part of the Bedouin diet, but many were nearly eradicated; these have been reintroduced and are cultivated organically, and a seed bank has been established for these precious plants. Hundreds of olive trees have been planted by local Bedouin high-school students, into soil enhanced and irrigated with the help of scientists from the Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research.
Women are working and taking part in the project’s planning—this is a real breakthrough among the Bedouins. Today Project Wadi Attir—the first-ever Bedouin agricultural cooperative in Israel—serves as a hub for eco-tourism, and as a model for Jewish-Bedouin collaboration. As Mayor al-Nabari puts it: “It is good for the people. It makes them feel good as citizens. It makes them proud to be part of Israel.”
Learn more about New Israeli tech, old Bedouin ways at Wadi Attir at Israel21c.org.